Completed Doctorates

Geothermal energy and policy incentive: Sustainable development in the agri-food sector. A study of twelve case countries
Margarita Kriger
Due to the environmental impacts of climate change, countries around the world have committed to shifting their energy supply from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, with geothermal energy having the potential to significantly meet the heating needs of agriculture and the food industry. This study shows a strong correlation between government support and the growth of geothermal energy use, with national policies having a greater impact than global and local policies.

Environmental laws as tools for effective management of Niger-Delta wetland: A case study of Upper Orashi forest
Iwebuke Edo
In the context of growing awareness of the value of wetlands and their loss, this study examines changes in the Upper Orashi Forest wetland to evaluate management policies in the region. Land cover analysis using Geographic Information Systems and remote sensing shows a continuous decline in wetland area between 2002 and 2019, which is confirmed by interviews with experts and local residents.

Population ecology of the Roman snail (Helix pomatia L. 1758) in Cottbus, Brandenburg
Claudia Tluste
The vineyard snail (Helix pomatia) is often perceived as a pest and is therefore considered an endangered species in Europe. This study investigates the role of the vineyard snail in the ecosystem and shows that it is an important food source for other animals, provides habitat for soil organisms and contributes to herbivory and nutrient cycling.

Investigation of the accumulation effects of heavy metals in oil palm plantation soils fertilized with anaerobically treated palm oil mill effluent in southern Nigeria
Osamudiamen Godwin Odigie
An accumulation of heavy metals was found in the soils of oil palm plantations in Ikpoba Okha, Nigeria, that were fertilised with palm oil mill effluent compared to control sites. Although the heavy metal concentrations were below acceptable limits, the long-term effects of the elevated concentrations could pose a potential risk, and close monitoring is recommended when using wastewater as an organic fertiliser.
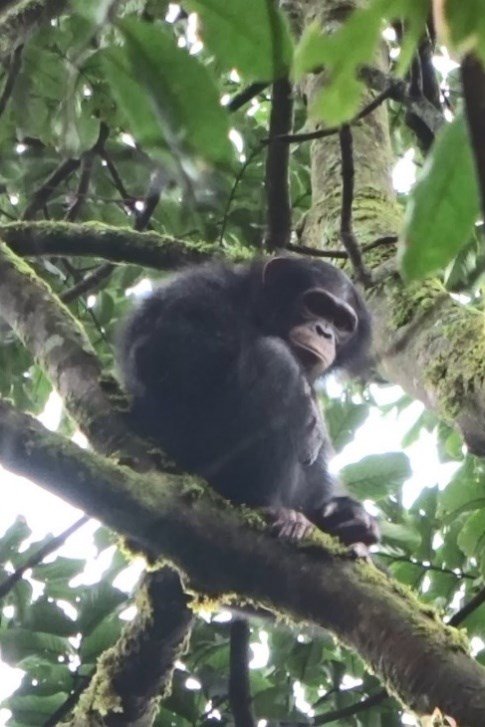

Conservation status and ecology of the Nigeria–Cameroon chimpanzee in Kom–Wum Forest Reserve, North–West Region, Cameroon
Chefor Fotang
Research in the Kom-Wum Forest Reserve in Cameroon aims to study the population size and ecology of the endangered Nigeria-Cameroon chimpanzee. It was found that only 8% of the area is suitable habitat. The study shows that the chimpanzees prefer tall, mature forests and use a variety of foraging tools, highlighting the need to reduce deforestation and poaching to ensure the conservation of this chimpanzee population.
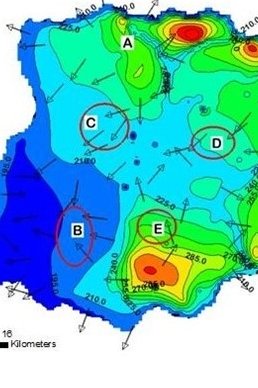
Hydrogeological assessment for evaluating the feasibility of managed aquifer recharge in Northeastern Ghana
Louis Boansi Okofo
In north-east Ghana, granite aquifers cover almost 80% of the annual groundwater demand, but are threatened by climate change and overexploitation, which affects the water supply and the livelihoods of farmers. A comprehensive hydrogeological study shows that the groundwater is mainly of good quality but has high nitrate concentrations. A numerical model confirms the possibility of groundwater recharge measures to raise water levels with regulated extraction.

Effects of forest restoration on ecosystem attributes in a post-mining area in Ghana
Frederick Gyasi Damptey
Restoration concepts for post-mining landscapes offer sustainable solutions for restoring biodiversity and ecosystem services, although the effects of such measures in the Afrotropical region have so far been insufficiently investigated. The study analyses soil characteristics, biodiversity and ecosystem services in an area in need of rehabilitation and investigates whether rehabilitation measures have a positive influence on these and whether synergies between different ecosystem services arise.

Sustainability assessment of bread production: The case of artisan bakeries in Germany
Sarkis Nehme
The study analyses the sustainability of the bread sector in Germany in the context of the German Sustainable Development Strategy 2030, using the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) framework to identify key indicators for assessment. While artisan bakeries contribute positively to sustainability, particularly in areas such as energy efficiency and waste reduction, bakery chains operate less flexibly and sustainably, but are more efficient in terms of productivity and market reach.

Possible synergy between FLEGT-VPA & REDD+ towards improving forest governance framework in Cameroon
Ernest Ako Enow
Illegal deforestation is a major challenge to sustainable forest management in the tropics and contributes to increased carbon dioxide emissions and biodiversity loss, which has led to negative impacts on the forest ecosystem, particularly in Cameroon since the 1980s. The study examines the synergies between the FLEGT-VPA and REDD+ policy initiatives to improve forest governance in Cameroon and highlights progress and challenges in the implementation of these programmes.

Use of close-to-nature surfactants and microbiological degradation for improving the remediation of crude oil contaminated soils in the Nigerian Niger-Delta
Mann Samuel Dido
The study investigates the potential of microbial and biosurfactant technology for the bioremediation of petroleum contamination in the Niger Delta of Nigeria, where the oil industry has caused significant environmental damage. The results show that co-treatment with mixed bacterial cultures and near-natural surfactants improves hydrocarbon degradation by up to 73.35 % while different bacterial strains successfully produce extracellular polymeric substances that contribute to emulsion formation.

Analysis of the relationship between spatial urban expansion and temperature utilising remote sensing and GIS techniques in the Accra and Kumasi Metropolises in Ghana
Bernard Fosu Frimpong
The study examines the relationship between urban expansion and temperature increase in the Ghanaian cities of Accra and Kumasi through a comprehensive analysis of land use and temperature changes. The results show a positive correlation between the expansion of urban areas at the expense of agricultural and forested areas and an increase in temperatures, indicating further urban warming.

Flood vulnerability assessment and adaptive capacity of smallholder farmers: A case study of the Orashi basin in the Niger Delta
Ikechukwu Mbachu
The study analyses flood risk for smallholder farmers in rural Nigeria and shows that deforestation has a significant impact on runoff volumes, while changes in rainfall patterns are less relevant. The results indicate that social inequality and poverty are the main factors that increase the vulnerability of smallholder farmers, while their adaptive capacity to flood events remains low due to weak social networks and economic disparities.

Evaluation of water situation and development of drinking water management plan for Aba City, Southeast Nigeria
Uche Dickson Ijioma
The quality of the main drinking water source in Aba, Nigeria is analysed. It is shown that urban land use practices affect water quality. By analysing water quality indicators and developing a thematic decision support management tool to identify monitoring zones and source protection areas, a cost-effective approach to improving drinking water quality in urban areas is proposed.

Assessment of the potentials of sustainability standards in the Nigerian industrial marine fisheries sector
Isa Olalekan Elegbede
The study analyses the impact of Friend of the Sea certification on the socio-economic and ecological systems of shrimp fisheries in Nigeria and finds that certified fishers achieve higher catches while catching less bycatch. Despite improvements in social conditions for fishers, the analysis shows that external factors and challenges affect the sustainability of the fishery, requiring a holistic review of the certification programme and collaboration with all stakeholders in the fisheries sector.

An assessment of the effectiveness of EIA system in Nigeria: A case study of Lagos State
Saheed Matemilola
The study assesses the effectiveness of the environmental impact assessment system in Nigeria, particularly in Lagos State, and identifies key constraints such as inadequate project coverage, bureaucratic hurdles and lack of inter-agency cooperation. Based on an analysis of questionnaires and environmental impact reports, a framework for improving effectiveness is proposed to address the challenges of the system and ensure better consideration of environmental impacts in major projects.

Evaluating policy impacts of minimum energy performance standards (MEPS) on Nigeria’s Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) to the Paris Agreement
Anayo Azubuike Ezeamama
The Nigerian government has developed Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEPS) to meet the energy and emissions reduction targets of the national contribution to the Paris Climate Agreement. A study carried out in Enugu shows that the current MEPS could reduce annual electricity demand by 37% and that stricter standards would contribute around 11.3% to the national emissions reduction target.

Modelling groundwater flow and contaminant transport for developing groundwater protection zone as panacea to groundwater contamination and water related diseases
Gregory Chimere Enyinna
In Abia, Nigeria, seasonal variations in groundwater quality were analysed and the impact of contamination from nearby sources was investigated. A significant correlation was found between water quality and diseases such as cholera and typhoid, highlighting the need for sustainable groundwater protection, regular quality control and improved sanitation systems to reduce contamination.

Environmental audit of gold mining: A case study of AngloGold Ashanti, Ghana
Kenneth Bedu-Addo
In Ghana, where more than six major gold mining companies and over a million small-scale miners operate, the study of the environmental and public health impacts of gold mining is becoming increasingly important as part of the 'AKOBEN Programme', a tool for monitoring and reviewing the environmental performance of gold mines. Although the programme assesses water pollution, it does not consider cumulative effects. No significant differences were found in the water quality of the Kwabrafo River before and after the introduction of the programme.

The potential of strategic environmental assessment to promote sustainable tourism in Tunisia: A dynamic policy management approach
Salma Halioui
Tourism is an important economic sector in Tunisia, supported by massive government investment since the 1960s, but faces major challenges due to mass tourism, political instability and terrorist attacks. In order to ensure the sustainability of the sector, the "Tourism Vision 3+1" was launched, and its effectiveness and efficiency were comprehensively analysed using methods such as Strategic Environmental Assessment and System Dynamics.

A novel integrated modelling approach to design cost-effective agri-environment schemes to prevent soil erosion and water pollution from cropland : a case study of Baishahe watershed in Shanxi Province, China
Zhengzheng Hao
Intensification of agricultural land use in China is leading to significant soil erosion and water pollution, with hillslope cropping accounting for more than half of the water pollution. To design cost-effective agri-environmental programmes, a spatially explicit integrated modelling approach is being developed that quantifies the environmental impacts of land use measures and takes into account farmer behaviour to identify effective measures to reduce soil erosion and nutrient pollution.

Development of single-stage solar-supported hyper-thermophilic anaerobic reactor for biogas production and disinfection of black water: A pilot case study of Terterkessim slum, Elmina-Ghana
Isaac Mbir Bryant
Rapid urbanisation in Ghana has led to the development of slums and a lack of sanitation, resulting in recurrent outbreaks of water and sanitation-related diseases such as cholera and typhoid. The project developed a solar-powered hyperthermophilic anaerobic biogas reactor for wastewater treatment, enabling high methane production and effective sanitation of wastewater.

Effects of helophyte species and system types in treatment of artificial acid mine drainage under carbon-deficient and sulphate-reducing conditions in laboratory-scale horizontal flow constructed wetlands
Ashirbad Mohanty
Surface water is used worldwide for agriculture and industry, but mining activities affect water quality due to high sulphate and heavy metal concentrations in acid mine drainage. This study investigates the sulphate and metal removal processes in constructed wetlands where hydrogen gas as an electron donor significantly increases the efficiency of sulphate and metal removal.

Analyzing the sustainability potential of Cameroonian palm oil residues for combustion in biomass-fired power plants
Bobbo Nfor Tansi
Increased palm oil production threatens tropical biodiversity and contributes to higher greenhouse gas emissions. This study examines the energy potential and environmental impact of solid palm oil residues from Cameroon's agricultural industry. While palm kernel shells offer the highest energy yield, oil palm trunks and fronds are less suitable for electricity generation. However, improved pre-treatment methods could enhance sustainability and energy efficiency.
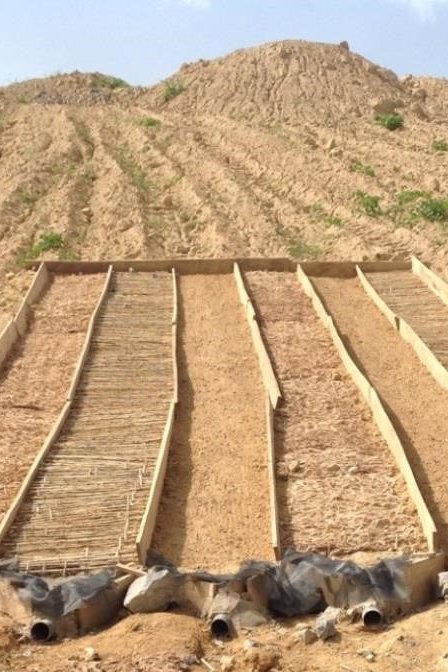

The potentials of biological geotextiles in erosion control and of substrate amendment on vegetation establishment during gold-mine reclamation in Ghana
Paul Kofi Nsiah
Effective planning and implementation of reclamation programmes in mining can reduce environmental damage and legal liability, but many mining sites in Ghana remain uncultivated or are unsuccessful. The use of geotextiles and manure is shown to have significant positive effects on soil stability, tree growth and vegetation cover, highlighting the need for appropriate reclamation measures for responsible mining.

Forest conservation and management practices in Cameroon: Case study of Bimbia-Bonadikombo Community Forest and Takamanda National Park
Regina Edawa Nyambi Anaka
The study compares the sustainability of a state and community-based forest management system in Cameroon and shows that the community-based system is more effective because local people are more willing to protect biodiversity. It recommends that the state system should promote greater inclusiveness and good governance to combat corruption and lack of transparency.

Analysis of Stakeholders’ Collaborative Process on Irrigated Agriculture: Weija Irrigation Scheme of Ghana
Henry Mensah
This research aims to identify best management practices in irrigated agriculture in Ghana and shows that weak communication and information sharing between stakeholders is a challenge. The results suggest that farmers benefit more from intra-institutional than inter-institutional collaboration, and that various factors such as gender and education influence collaboration processes.

Economic valuation and analysis of climate change adaption measures in sub-Saharan African agriculture: A case study of Makueni County, Kenya
Mary Nthambi
Recurrent droughts in Kenya have a severe impact on the agricultural sector and threaten the food security of millions of people. This study assesses economic climate adaptation measures and governance structures in Makueni County, identifies farmers' preferred adaptation strategies, and shows that non-governmental organisations should play an important role in implementing these measures.

Assessing the impact of sustainability standards as a strategy for livelihood sustainability in the cocoa industry: In the south west region of Cameroon
Eric Ambe Asoh
The study analyses the socio-economic impact of Fairtrade support on smallholder cocoa farmers in South West Cameroon and shows that Fairtrade cocoa farmers have more farm equipment and better access to credit than conventional farmers. Despite positive impacts such as more advanced farming techniques, individual socio-economic impacts are minimal and do not contribute significantly to the regional value chain.

Adaptation to climate change in developing countries: Institutional challenges and opportunities for Nigeria’s Niger Delta region
Chika Ubaldus Ogbonna
The study analyses the challenges and barriers to climate change adaptation in the Niger Delta, which is highly vulnerable to climate variability, and identifies inadequate institutional mandates, weak inter-institutional cooperation and lack of political will as the main problems. It recommends reviewing existing regulatory instruments, providing financial resources and raising public awareness to create opportunities for sustainable development in the region.

What does it take to treat municipal wastewater in developing countries? An econometric analysis of Mexican municipalities
Lutz Philip Hecker
Water pollution is a major problem in developing countries, where 2.2 billion people fall ill every year as a result of inadequate or non-existent wastewater treatment. The social factors influencing urban wastewater treatment in Mexican municipalities are analysed and geographical spillover effects are identified. Environmental federalism and institutional aspects are identified as important influencing factors, while education and ethnic heterogeneity have little influence.

Enhancing renewable energy deployment in Malawi through climate finance instruments: Policy challenges and prospects
Dumisani Chirambo
Malawi, one of Africa's least developed countries, has an electrification rate of only 9% and suffers from unreliable power supply, which hinders the country's productivity and sustainable economic growth. It is recommended that a Renewable Energy and Climate Finance Promotion Company be established to mobilise finance for renewable energy projects and promote national interests in energy policy.

Brazil in the global forest governance: The Brazilian initiative of developing a national strategy on REDD+ policies
Patricia Gallo Barbosa Lima
The dissertation analyses the development of the REDD+ mechanism as a national strategy in Brazil and identifies key challenges and policy constraints. It recommends multi-level and sustainable approaches to landscape governance to improve REDD+ implementation and address the country's environmental challenges.

Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM): The Case Study of the Far-North Region, Cameroon
Ambe Emmanuel Cheo
The Far-North Region of Cameroon suffers from extreme water scarcity, mainly due to poor water management rather than climate change. Inappropriate agriculture and urbanisation exacerbate the situation. Integrated water resource management and measures such as rainwater harvesting and artificial groundwater recharge are therefore recommended to increase water availability and promote sustainable water management in the region.

Developing a conceptual solution for domestic wastewater management in developing countries: Kumasi (Ghana) as a case study
Kwaku Boakye Apau
The study develops evaluation criteria for the selection of suitable wastewater treatment systems, especially for developing countries, and evaluates four technologies (wastewater ponds, septic tanks, constructed wetlands and reed bed treatment plants) in terms of their efficiency, reliability and resource use. The indicators and their weighting have a significant impact on the choice of the best technology, with constructed wetlands emerging as the optimal solution in a realistic scenario.

Risk management of nanotechnologies within German legislation
Joel Goebelbecker
Nanotechnology is considered one of the most important fields of technology for the future. The growing industry is constantly producing new materials, but little is known about their effects. In principle, they are subject to the current regulations of the German legal system, but the question is whether the existing regulations are sufficient or whether there are regulatory gaps. Although nanomaterials are in many cases covered by the existing legal framework, the existing regulations must be regarded as inadequate for dealing with all types of nanomaterials in the short and long term.

Added value of voluntary sustainability standards for non-traditional export products in the agricultural sector of Ghana
David Yakubu Anambam
Voluntary sustainability standards are an innovative, market-based approach to promoting sustainable production and business practices. Fairtrade is one such standard, combatting poverty and empowering producers through trade. This study examines the impact of Fairtrade on poverty reduction. It analyses the financial and non-financial support that Fairtrade provides to small-scale producers, focusing on shea producers in northern Ghana.

Hygienization of enteropathogens contaminated biowaste for safer biological treatments
Jacob Paul Muhondwa
The project is investigating the sterilisation rate of pathogenic micro-organisms in organic waste and developing alternative sanitisation methods, with conventional methods such as acid and lime treatment and pasteurisation showing effective results in eliminating E. coli and Salmonella. In addition, the biological and sustainable use of potato peel is being investigated, with anaerobic digestion enabling significant biogas production that can help meet energy needs while providing valuable fertiliser for agriculture.

Influence of the German renewable energy and climate policies on onshore wind energy generation: Implementation options in Cameroon
Emmanuel Wanki Ateghang
The German government has set ambitious targets for the expansion of wind energy, but as the largest wind energy market in the EU, Germany faces challenges such as limited land and rising electricity prices. The study assesses the impact of German climate policy on onshore wind energy production and analyses the applicability of the German model in Cameroon.

Optimization of nitrogen removal in various vertical flow constructed wetland designs and application of treated wastewater for reuse in irrigation in Jordan
Ghaida Abdallat
In arid countries, reuse of treated water for irrigation is important, and constructed wetlands as a decentralised wastewater treatment technology and their effects on soil properties are investigated. The study shows that different systems in Germany and Jordan can achieve high treatment performance, but that there are challenges in nitrogen removal.

Implementation of environmental taxation in Ghana
Alex Moyem Kombat
To reduce environmental pollution and generate revenue, Ghana has introduced various environmental taxes, including those on plastic consumption, old vehicles and mineral oil. This study examined the implementation phases, the actors involved and the effectiveness of these taxes. While the taxes are cost-effective and promote international technology transfer, the environmental objectives have not yet been fully realised. Recommendations are made on how to exploit their potential for controlling and preventing environmental pollution more effectively.

Statistical analysis of extreme climate events in Brandenburg
Ni An
This study evaluates the performance of the fine-resolution CLM model for Brandenburg, Germany, by developing a bias correction procedure focusing on extreme events such as daily temperatures and precipitation. The results show that the correction procedure is effective in significantly reducing the influence of extreme daily temperatures and indicate that extreme temperatures and precipitation will increase in both intensity and frequency in the 21st century.

Sustainable development of domestic water supply in emerging megacities: The case of the city of Guadalajara, Mexico
Juan Pablo Gómez Jáuregui Abdó
Water is a critical resource for the development of urban areas. The study of Guadalajara's water supply shows that the city is currently unsustainable. The main problems identified are inadequate wastewater treatment, water losses in the distribution system and the limited availability of water from Lake Chapala.

Impact of climate change on irrigation water resources management in northern Ghana: A case study of the Upper West Region
Emmanuel Amankwah
Climate change is increasingly threatening subsistence farming in northern Ghana. This is leading to lower crop yields and food insecurity. As part of the study, climate data was analysed and 400 farmers in the Upper West region were surveyed. The results demonstrate the impact of deforestation and bushfires on agriculture. The study emphasises the importance of combining indigenous knowledge with climate science to develop sustainable, community-driven adaptation strategies. It also provides policy recommendations to help farmers cope with climate change.

The effects of habitat heterogeneity and human influences on the diversity, abundance, and distribution of large mammals: The case of Deng Deng National Park, Cameroon
Mercy Nambu Diangha
Studies have been carried out in Deng Deng National Park to analyse the spatial and temporal patterns of habitats and the impact of human activities on large mammal populations, using methods such as distance sampling and GIS analysis. The results showed a high degree of habitat heterogeneity and a significant decline in species diversity in areas of intensive human activity, while the first detection of elephants highlights the importance of the park for large mammal conservation.
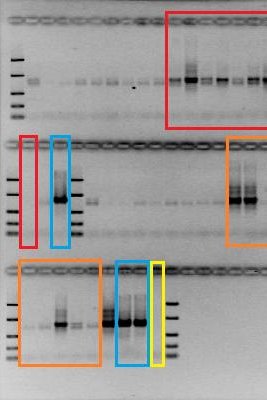
Microbial nitrogen transformations in constructed wetlands treating contaminated groundwater
Oksana Coban
Groundwater is an important source of drinking and process water, but can be affected by ammonium, which is toxic to fish. Constructed wetlands provide an effective method of removing ammonium through microbial degradation. The study shows that nitrification and denitrification are the main processes for ammonium removal, while anaerobic ammonium oxidation plays a less important role. The study provides valuable insights into nitrogen transformations and supports technological improvements in wastewater treatment.

Community-based forest management and changing gender roles in a patriarchal society in Cameroon: The case of Korup and Bechati forest areas
Lilian Wopong Nkengla
Forests are an important source of livelihoods for many rural communities in developing countries, but resources are threatened by various changes, leading to forest policy reform in Cameroon in 1994. The study shows that men and women have different roles and interests in forest management, with women often underrepresented. To improve their participation, inclusive policies and a change in gender roles are needed.
