Completed Doctorates

Greening the institutions: Curatorial activism’s impact on environmental awareness in South India
Shubhani
This study examines the role of curators in the Indian context with a view to improving the relationship between audiences and environmental art projects through curatorial activism. The study analyses how curators can strengthen public communication about environmental crises and climate science through events and exhibitions, in their roles as researchers, educators and mediators. It also evaluates the profound impact of relationship-building strategies on audience participation.

An intersection of heritagisation and securitisation in postcolonial mexican communities
Laura Cristina Revilla Sanchez
From a local perspective, particularly in Mexico, the relationship between cultural heritage and security within postcolonial communities is examined. Ethnographic methods and collective case studies are used to examine the interactions between cultural heritage and security practices in times of crime and violence. The aim is to understand the influence of heritage and security practices, and to shed light on their impact on community building in a postcolonial context.

Cultural heritage and public-private partnerships: The rationales, limitations and potentials
Mahmoud Ahmed Bakry Abdou
Public-private partnerships offer governments an attractive option for preserving and financing cultural heritage sites. However, little literature exists on their mechanisms and challenges. This study examines the associated advantages and complex challenges, including political commitment, decision-making processes, and misunderstandings. It emphasises that overcoming these obstacles requires comprehensive efforts, depending on factors such as public support and stable market conditions.

The Ain Juj Water Channel in Baalbek: Merits for the cultural heritage through the evaluation of the channel geometry, geochemical analyses of carbonate deposits, and the determination of chronostratigraphy
Juliane Schmidt
For the first time, the use of the Ain Juj water channel in Baalbek, which is connected to the Temple of Jupiter, has been accurately dated to prehistoric times. These findings support the existence of early settlements in the area and shed new light on settlement activities in Baalbek. The results should also help to ensure the spring and canal, which are located outside the UNESCO World Heritage Site, are better protected.

The contribution of community involvement in heritage management: A cultural mapping project
Esraa Fathy Abdelaziz Alhadad
The project explores community participation in heritage management as a solution for a more effective management system, specifically using the example of the religious complex in historic Cairo. Using a cultural mapping approach, community participation in heritage management will be analysed to gain critical insights into collaborative decision-making and the drivers of participation.
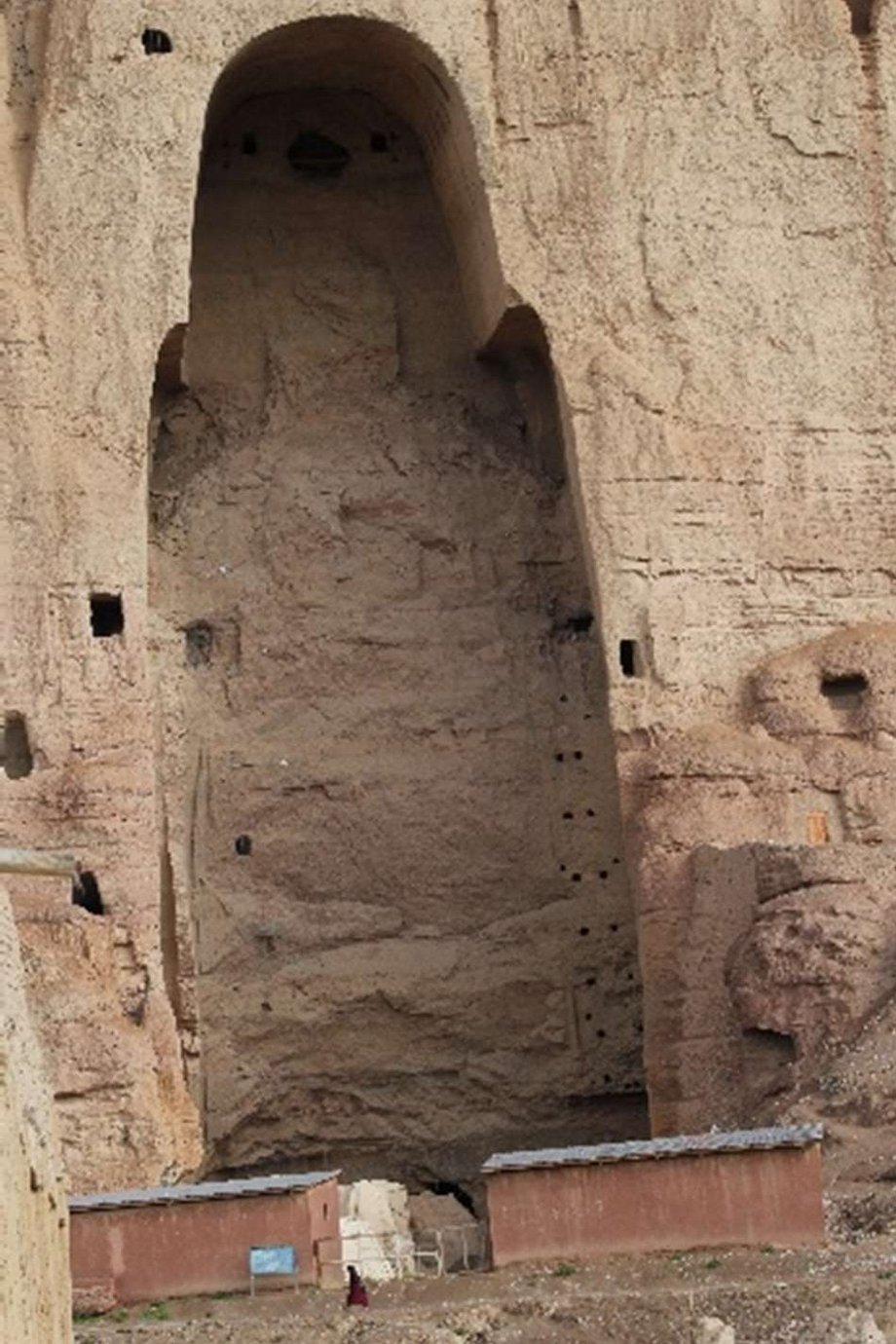

Challenges of heritage risk-based management in Post-war Afghanistan: The case study of Bamiyan Valley
Reza Sharifi
Armed conflict has severely threatened Afghanistan's cultural heritage over the past four decades, causing both direct destruction and increased vulnerability to other risks such as natural disasters. This dissertation develops a methodological framework for cultural heritage risk assessment that aims to quantify the threats and understand the values of the heritage to enable effective mitigation measures and protection of threatened sites in future conflicts.
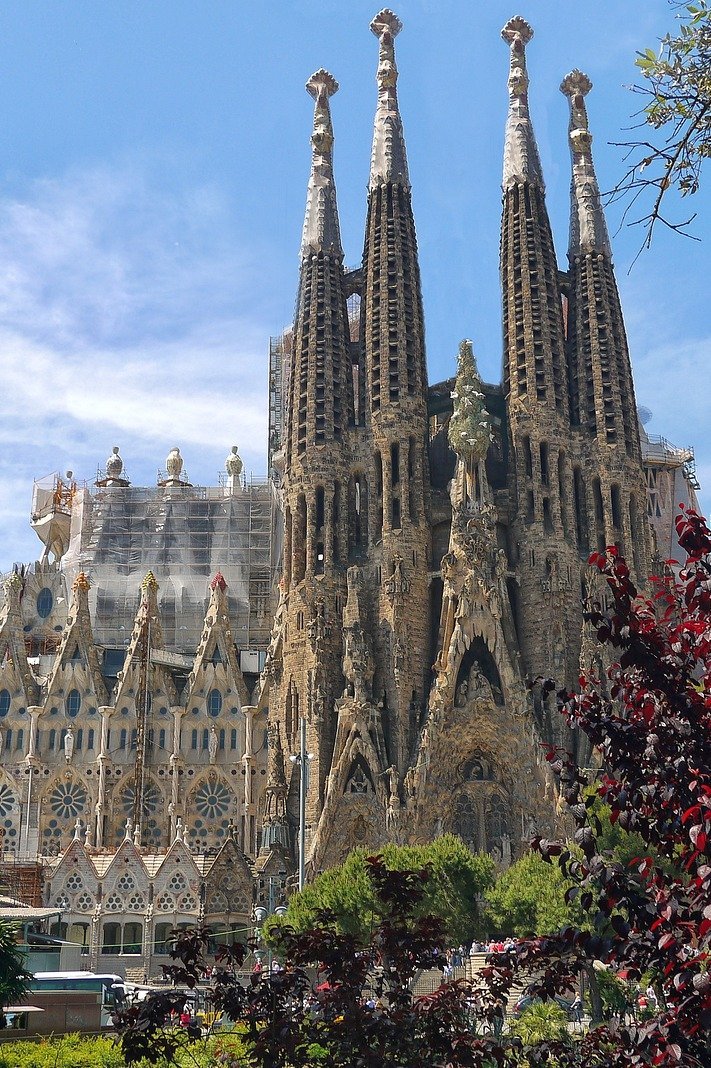

Towards significance assessment of the Sagrada Familia for the conservation of a cultural heritage masterpiece
Hina Hasnain
The conservation of the Sagrada Familia is a complex challenge, as the original vision of the architect must be preserved and adapted to modern needs without compromising the building's significance and authenticity. The project explores the multi-layered meaning of the Sagrada Familia over time, the various influences on its design and construction, and the holistic, multidisciplinary approach to conservation that takes into account cultural, technical and religious aspects.

Role of community in managing cultural heritage tourism in historical quarters of Delhi: Case studies of Nizamudinn Basti and Shahjahanabad
Ekta Chauhan
The thesis examines the role of communities in heritage tourism decision-making in New Delhi, India, and addresses issues of barriers, motivations and collective action within the IAD-NAAS (Institutional Analysis and Development-Network of Adjacent Action Situations) framework. Qualitative research methods will be used to gain a comprehensive understanding of citizen participation, enabling heritage tourism initiatives to become more democratic and inclusive.
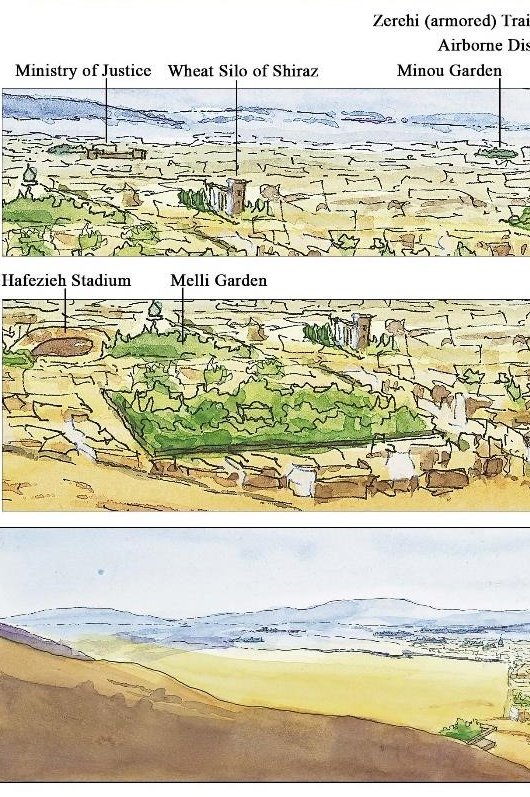
Safeguarding the visual integrity of the historic urban landscape (HUL) through contextualised instrument development: The case study of Shiraz
Farnaz Mohseni
The feasibility of the Historic Urban Landscape (HUL) concept is investigated through a case study in Shiraz, Iran, focusing on the visual integrity of the historic urban landscape. Through a mixed-methods research approach, thirteen viewpoints, 137 landmarks and key factors were identified to develop a contextual tool for the protection and development of the historic urban landscape.

The formal primary educational system and the safeguarding of intangible cultural heritage in Africa: Case of the Far North Region of Cameroon
Abdel Kader Barounga
The thesis examines how intangible cultural heritage can be integrated into the formal primary education system in the Far North Region of Cameroon in order to preserve ethno-cultural identities. Using a case study in the Kolara District, it examines how declining knowledge of ethnocultural heritage can be reconciled with the formal education system to provide culturally enriched education for children.

A metamodel for heritage-based urban development
Matthias Ripp
The thesis develops a meta-model for the universal application of cultural heritage in urban development processes, based on successful models from different contexts. By combining grounded theory, design research methodology and John P. Van Gigch's meta-model theory, an abstract and applicable tool has been created that maps the complexities and relationships in heritage-based urban development processes.

Shared history, urban landscapes, and local arts and crafts: Perspectives on cultural heritage as a means of sustainable community development in Iringa, Tanzania
Jan Küver
The link between cultural heritage and sustainable community development in Iringa, Tanzania is analysed using ethnographic methods and long-term project practice. Three specific themes of investigation are highlighted: historical memory and interpretation, socio-spatial heritage, and economic use of cultural heritage, to show how targeted cultural preservation strategies can support community development.
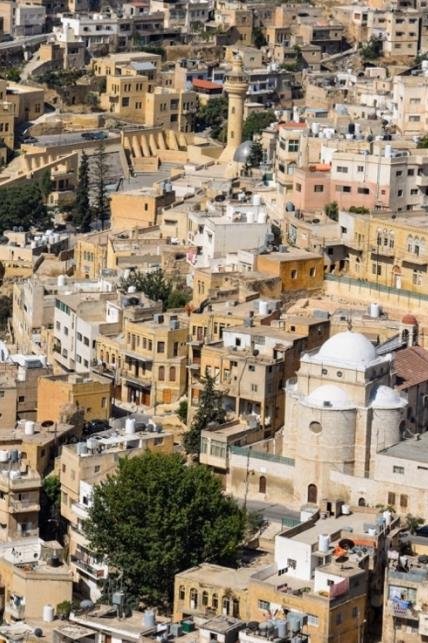

A heritage-based community process trough the historic urban landscape recommendation: The historic center of As-Salt in Jordan
Zain A. Hajahjah
The research explores the Historic Urban Landscape (HUL) approach to promoting community development in historic urban centres, specifically using the example of As-Salt in Jordan. Through literature review, interviews and surveys, a theoretical model is developed to analyse community integration in urban heritage conservation and to derive recommendations for a holistic and integrated approach.
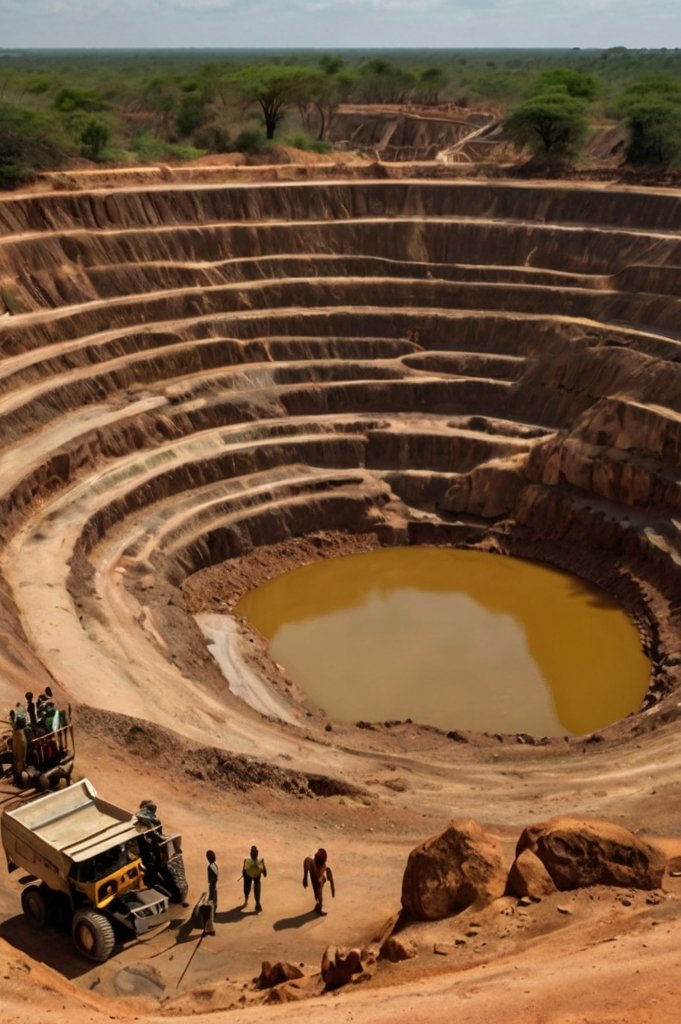

Mining in the context of African World Heritage cultural landscapes: An assessment of management planning effectiveness
Oris Chapinga Malijani
It examines the impact of mining activities on cultural landscapes in sub-Saharan Africa and highlights the need for a holistic management approach to their long-term conservation. Using case studies such as the Mulanje Mountain Cultural Landscape in Malawi and the Mapungubwe Cultural Landscape in South Africa, it explores management approaches to address the challenges posed by mining developments and to preserve the cultural and natural heritage values of the landscapes.
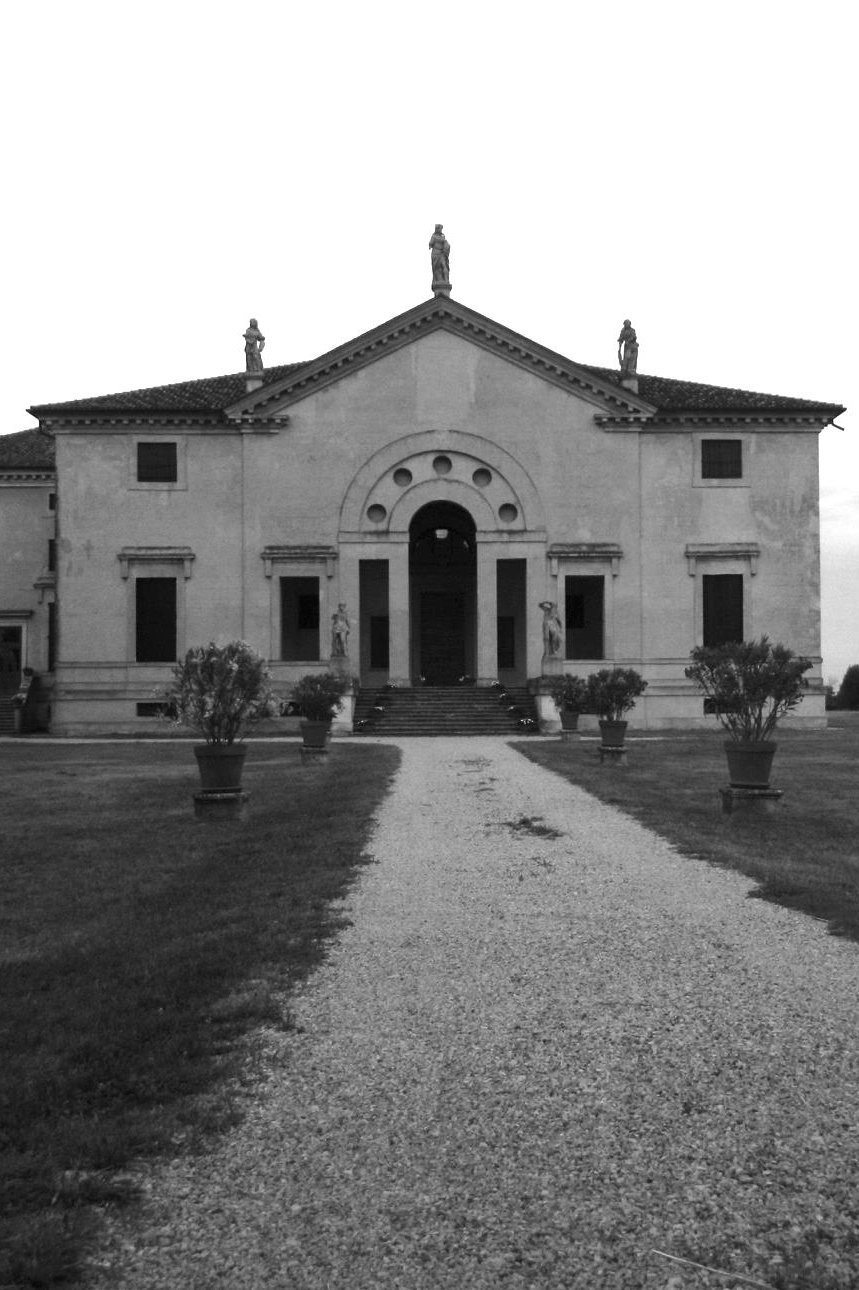

Scale dissonances between local and world heritage: The rural landscape of the Palladian villa
Valentina Torelli
The research analyses the visual representation of the landscape of Palladian villas as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Veneto, Italy, and reveals dissonances between global and local perspectives. It recommends that the World Heritage protection scheme be reformulated, that the local population be involved in the management plan, and that the local agricultural practice be considered as a continuous cultural landscape in order to allow for an integrated conservation of the heritage in its socio-historical context.
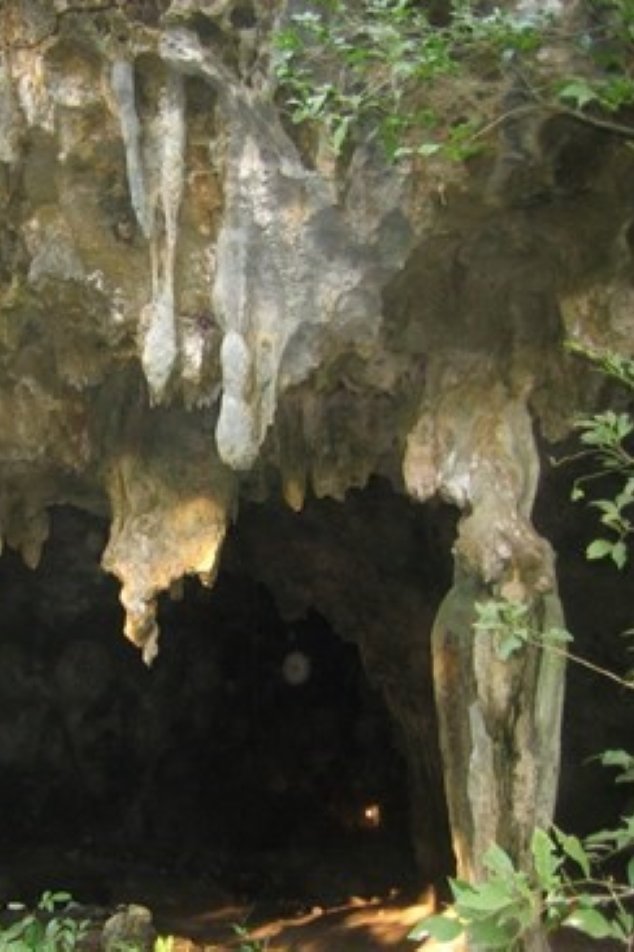

Sacred Limestone Caves: Management and the use of sacred heritage places in limestone cave areas along the Swahili Coast of Indian Ocean in Tanzania
Maximilian Felix Chami
The research examines the use and management of limestone caves along the Swahili coast of Tanzania as sacred sites used by Swahili communities for ritual practices. It finds that issues such as inadequate conservation measures, lack of management plans and encroachment by tourism and research are disrupting the link between local communities and their cultural heritage, and proposes a framework for improved management to ensure that local communities continue to have access to their religious sites.
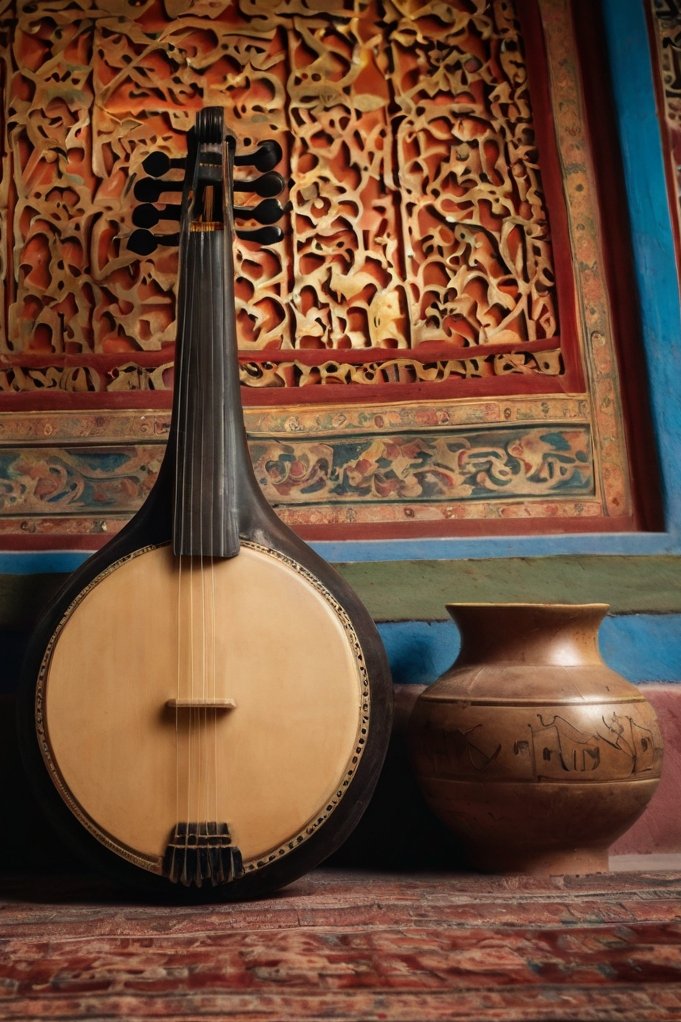

The cultural production of musical heritage and cultural identity in socialist China. The case of Uyghur Muqam Music
Sijin Chen
The thesis analyses the development of Uyghur Muqam music, especially after 1945 during the Proletarian Cultural Revolution, as a medium for spreading revolutionary messages in socialist China. It seeks to understand how the once endangered Muqam music not only survived, but actually spread and expanded its significance for Uyghur cultural identity during this critical period.
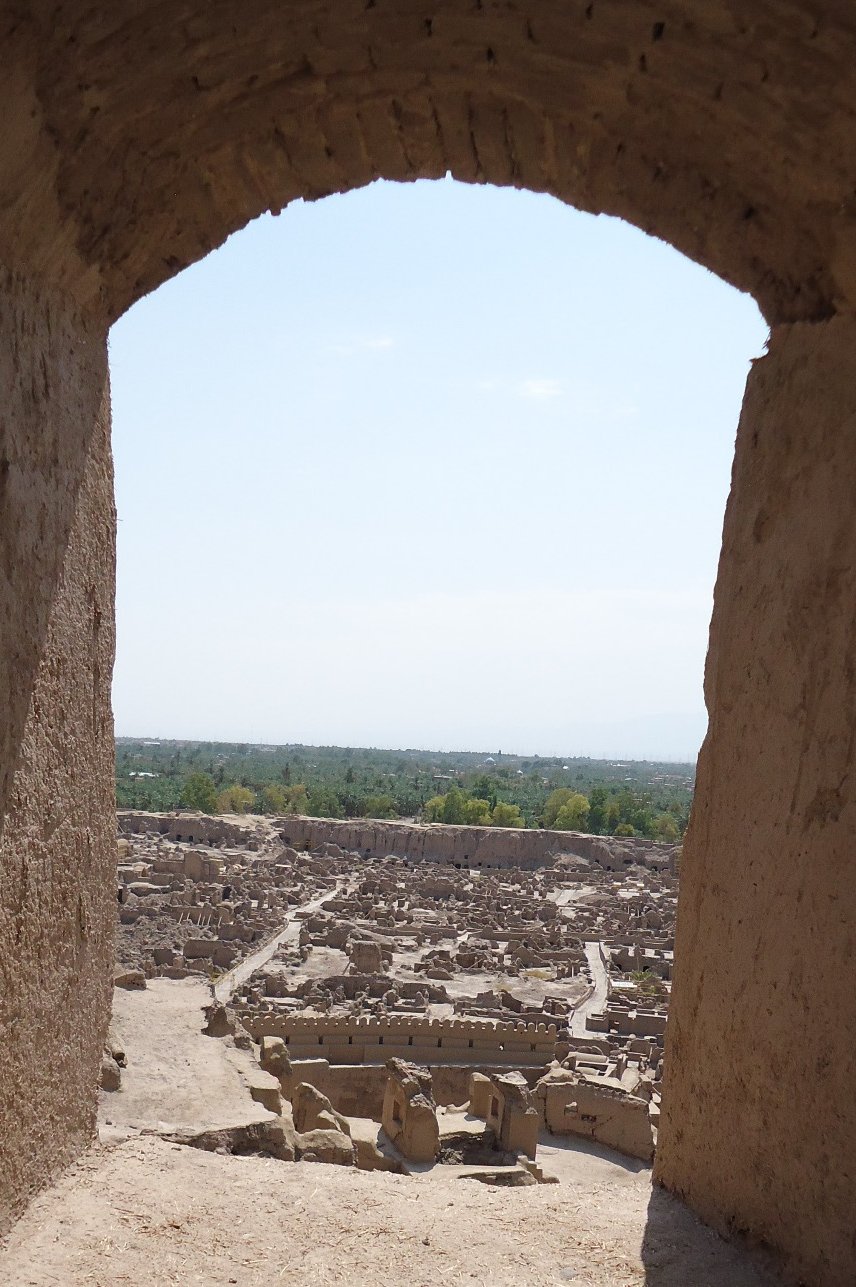

Earthquake disaster risk assessment for cultural World Heritage sites: The case of “Bam and its cultural landscape” in Iran
Mohammad Ravankhah
The research focuses on the development of a cultural heritage risk index for the World Heritage Site 'Bam and its Cultural Landscape' in Iran to assess the impact of earthquakes on cultural heritage and to develop site-specific risk mitigation strategies. By integrating hazard, exposure and vulnerability into the index and using a Geographical Information System (GIS) to visualise risk, a practical tool will be created for professionals to facilitate risk management plans for the protection of cultural heritage.
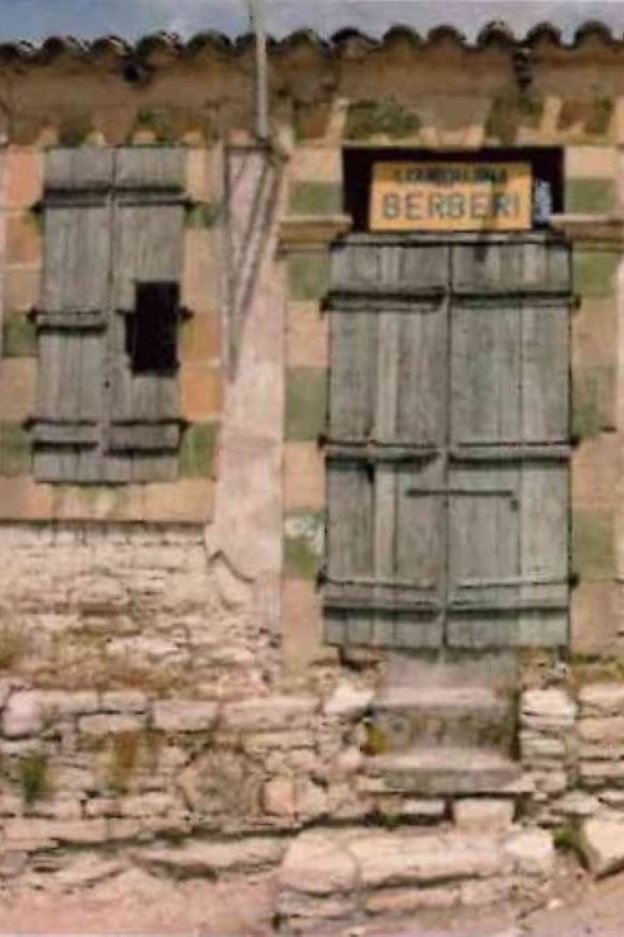

Conservation of vernacular architecture in the context of climate change. A study of Louroujina (Akincilar) Village, Cyprus
Obafemi Alaba Paul Olukoya
The thesis analyses the protection of indigenous architecture in the Eastern Mediterranean (Louroujina, Cyprus) from the risk factors of climate change through a value-based approach. The projected climate change scenario shows the strong impact on the material characteristics of the different typologies of indigenous architecture, which are particularly vulnerable due to the abandonment of buildings, the low economic power, the disappearance of the intangible heritage, the population decline and the lack of traditional knowledge and skills for reconstruction.

The valorisation of intangible cultural heritage. A Bourdieusian approach to the developmental potentials of heritage
Marlen Meißner
Against the background of the UNESCO Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage (2003), the thesis conceptualises the development potentials of intangible cultural heritage using Pierre Bourdieu's "Theory of Practice". The main objective is to systematise the development potentials as "drivers" and "enablers" within a methodological frame of reference in order to support their active valorisation in the context of the Convention and beyond.
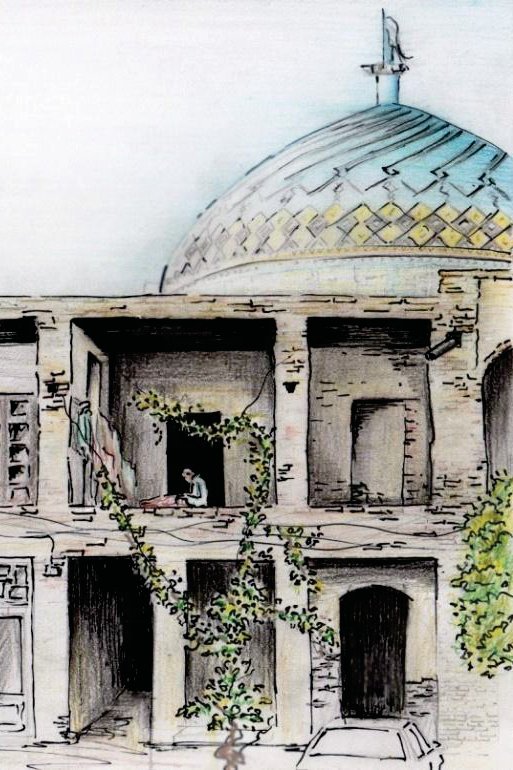

The Iranian bazaar as a public place: A reintegrative approach and a method applied towards the case study of the Tabriz bazaar
Solmaz Yadollahi
Using the example of the bazaar in Tabriz, which is the largest intact bazaar in Iran in both social and spatial terms, the project analyses how an Iranian bazaar is structured and functions as a public space in a modern city. Using qualitative and quantitative research approaches, the cultural, legal, physical and functional backgrounds of the bazaar will be documented and mapped.

Shared heritage: Sacred landscapes of Crimea, their development and protection in the multicultural context
Dariya Afanasyeva
The thesis examines the religious and cultural diversity of the Crimea by analysing sacred sites as an expression of this diversity and their significance for the ethno-religious groups of the peninsula. It explores the relationship between religion, landscape and memory, as well as the development and protection of sacred sites over time, using case studies such as the Assumption Monastery and the cave city of Chufut-Kale.

Screening Intangible Heritage: Media, heritage and representation: The case of Kutiyattam Sanskrit Theatre, India
Shina-Nancy Erlewein
It examines the role of audio-visual media in representing intangible cultural heritage, with particular reference to Kutiyattam Sanskrit theatre, and offers a blueprint for its sustainable use and development. It highlights the opportunities and risks of media representation and emphasises the importance of culture-specific coding and community participation in the preservation of cultural heritage through audio-visual media.

Conflictive delisting process of a World Heritage Site in Germany: The case of the Dresden Elbe Valley
Bénédicte Gaillard
The conflict between the Federal Republic of Germany and UNESCO in the case of the Dresden Elbe Valley, caused by the construction of the Waldschlößchenbrücke in the Dresden World Heritage Site, is analysed. In particular, the reasons for the conflict and the impossibility of a compromise will be demonstrated through a historical and legal analysis. In order to avoid similar conflicts in the future, suggestions for improvement will be presented to the City of Dresden, the Free State of Saxony, the Federal Republic of Germany and UNESCO.

The digital "Memory of the World": An exploration of documentary practices in the age of digital technology
Anca Claudia Prodan
This study critically analyses the use of digital technology in UNESCO's Memory of the World programme to explore its possibilities and limitations. Based on Harold Innis' Medium Theory, it concludes that an overemphasis on digital access can limit the overall intentions of the programme and proposes solutions to integrate digital technology in line with the programme's philosophy.

About the conservation of cultural landscapes: Sustainability or unviability? A comparative study on the emergent landscape management in heritage sites in mountain regions: The Andes and the Pyrenees
Maya Ishizawa
The study analyses the concepts of cultural landscape conservation using two case studies from mountainous regions, looking at different models of nature and past conservation. The dissertation questions the relevance of the concepts of 'conservation' and 'sustainability' and instead proposes landscape management as an alternative that simultaneously implies 'conservation' and adaptation to change.

From “Feudal Rubbish” to “National Treasure”: The transformation and safeguarding of intangible cultural heritage of China. A case study of Huanxian Daoqing Shadow Theatre
Chang Liu
The thesis examines the transformation of Huanxing Daoqing Shadow Theatre in China from a despised to a nationally valued cultural heritage by studying government archives and conducting interviews with traditional Daoqing artists. By analysing the social role, cultural value and transmission of the understanding of Daoqing, the study shows how a collaborative effort by government and community contributes to the preservation of this intangible cultural heritage and offers insights for dealing with similar heritage preservation challenges in China.

Intangible cultural heritage of dance as medium for intercultural dialogue: Culture assimilator reinterpreted
Chee Meng Wong
The study explores two models of using cultural heritage in intercultural dialogue: a transcultural model that focuses on creative engagement to overcome cultural differences, and a multicultural model that focuses on mutual understanding and respect. The role of Indian dance in Singapore is analysed to explore aspects of open-mindedness and empathy in intercultural learning and to deconstruct cultural differences.

The Birth of Brazilianism: The stereotypical representation of Brazil in the context of cultural imperialism and media concentration
Andreza André Da Rocha
The representation of Brazil in mainstream American cinema is based on stereotypical narratives, while Brazilian films that more authentically portray the country's diversity receive little international distribution. This study examines the use of stereotypes in Hollywood films about Brazil and argues for a revival of the debate about a more just world order in the field of communication.

Understanding heritage: A constructivist approach to heritage interpretation as a mechanism for understanding heritage sites
Iryna Shalaginova
The study examines visitor-centred interpretation of historic sites from a constructivist perspective, focusing on communicative processes and the fulfilment of orientation expectations to promote understanding. The role of culture in this process is also explored, and a three-component model of communication is proposed to enable effective communication and understanding between different cultural groups.
