Development of a load- and performance-based management concept with an analysis and consulting system for the co-treatment of process wastewater and faeces using the example of the Cott bus wastewater treatment plant
Brief description of the content:
A new operating and management concept is being developed for the Cottbus wastewater treatment plant, which includes the use of a simulation system coupled with an expert system. The aim is to optimize operation and increase operational stability, taking into account the performance-dependent addition of process water from sludge treatment and faeces.
Responsible for the process engineering part: Dipl.-Ing. Silke Osterburg
Task of the LS Abwassertechnik:
Process Engineering evaluation of the tests already carried out, process engineering supervision of the tests still to be carried out and cooperation in the preparation of the entire final report
Duration:
Funding institution: 01.01.92 to 31.05.97;
LS Abwassertechnik: 01.11.96 - 31.05.97;
ABB Automatisierungsanlagen Cottbus GmbH
Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Project Management Agency of the BMBF for Water Technology and Sludge Treatment
"Development of a post-treatment process for nutrient elimination for wastewater treatment plants in rural areas with the aim of safe discharge into sensitive water bodies or groundwater"
Author Dipl.-Ing. F. Rolf
Introduction:
Municipal wastewater treatment plants in rural areas, most of which belong to size classes 1 and 2, treat wastewater according to the generally recognized rules of technology, even if they do not achieve nutrient elimination and a less extensive removal of pollutants. Technical and economic problems arise when stricter requirements are placed on the purification performance of these annexes, e.g. when discharging into sensitive waters or for the protection of coastal waters.
The application of the proven Process Engineering of large wastewater treatment plants on a small scale only makes sense in rare cases, mainly for cost reasons. Against this background, the Chair of Wastewater Technology at BTU Cottbus has developed a process concept aimed at cost-effective advanced wastewater treatment in wastewater treatment plants of size classes 1 and 2.
Process concept:
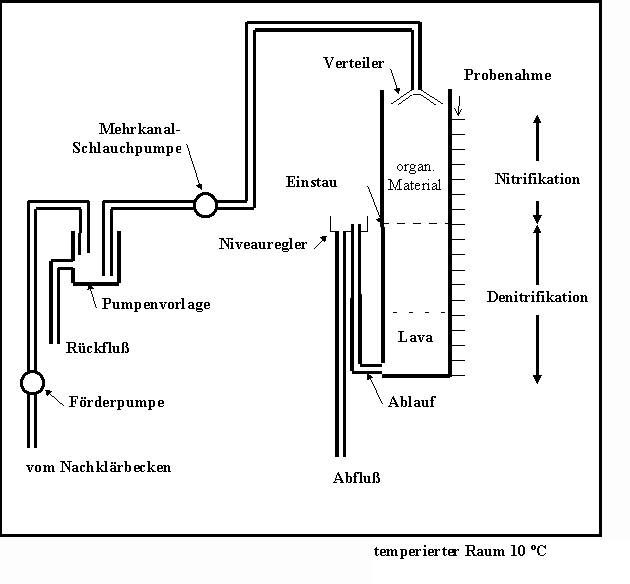
Basic treatment is carried out using conventional methods that have been tried and tested in rural areas, such as oxidation ditches, trickling filter systems, pond systems or constructed wetlands. Further treatment, including nutrient elimination, is carried out in a fixed-bed reactor based on the following principle: The elimination processes that take place during natural soil passage are controlled in a reactor separate from the subsoil and brought to bear in an optimized manner.
The optimization approaches of denitrification and phosphate elimination are particularly characteristic of the process. Denitrification is achieved through the use of a degradable solids matrix, phosphate elimination through the use of ferrous residues.
Trial operation:
A small-scale pilot plant (six columns 2 m high and 25 cm in diameter) has been in operation for around two years to test "clear water percolation".
The test results to date show that a BOD5 effluent concentration of less than 7 mg/l can be achieved permanently and safely. The reduction of the COD concentration to less than 30 mg/l is also achievable, but causes difficulties when using fixed bed materials with a high lignin content due to the refractory components introduced. Nitrification can be carried out without any problems at sufficient temperatures. The success of denitrification is heavily dependent on the availability of an easily degradable substrate. The suitability and optimal use of various filter material components and combinations is currently being tested. The elimination of phosphates could be achieved both by adding waterworks gravel and by using iron filings. The desired elimination performance appears to be achievable by adjusting the quantity of ferrous residues added.
Technical operation:
A technical test plant for up to 300 PE is currently being built on the basis of the findings.
The construction of the (semi-)technical test plant is being funded by the German Federal Environmental Foundation.
Sewage sludge utilization with straw admixture
Agricultural sewage sludge utilization with straw admixture and rotting or rapid composting
Co-treatment of faecal sludge in small wastewater treatment plants
Testing the performance limit for faecal sludge co-treatment in an SBR plant of size class 2 with a high proportion of commercial wastewater.
Phosphate elimination with ferrous residues
Column tests to determine design parameters for P elimination with waterworks gravel, iron filings, waste fraction from magnetic separation, etc.