Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolysis
The generation of hydrogen by anion exchange membrane electrolysis (AEMEL) of water is an emerging technology for the furture high-power density and low-cost production of hydrogen. With an AEMEL test rig, we conduct research on the following topics:
- Component tests (electrodes, catalysts, membranes, end and bipolar plates, cell frames, sealings)
- Investigation of different dynamic modes of operation
- In-operando analysis at single-cell level and at short-stack level
- H2 purity analysis
- Multi-scale simulation models (incl. model verification)
Technical specifications
- Operational pressure: atmospheric
- Operational temperature: max. 80 °C
- Usable electrolytes:
- DI water
- Max. 1 M KOH
- Adjustable volume flow rate in electrolyte circle: max. 3 l/min
- Electrolyte feed mode: simultaneous on cathode and anode side
- Operating current (DC): up to 200 A extensible up to 340 A)
- H2 production rate: up to 83 Nl/h (at 200 A)
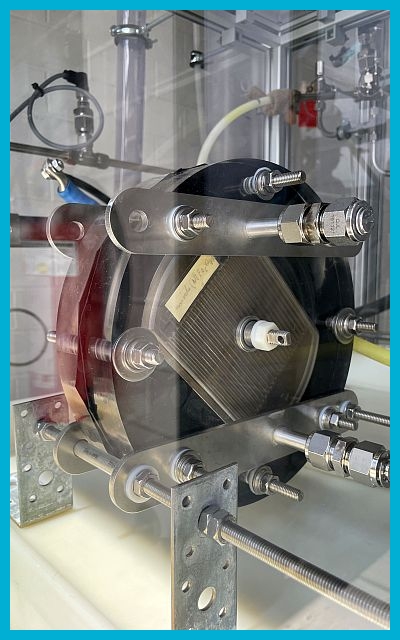

Cell configuration
- Single cell or short-stack
- Frame material: PMMA
- Active catalyst area: up to 100 cm2
- Testable electrode substrates
- Carbon papers or cloths
- Foams
- Meshes
- Distance electrode-membrane: zero-gap
- Distance electrode-flowfield: zero-gap up to 1 mm
- In-operando investigations: Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and further electrochemical measurement methodes (GAMRY potentiostat & booster)
